2.1 Making a hierarchical structure
We can use the make_structure function to create nested and crossed hierarchical data structures. The make_structure function only produces balanced data structures, but these can be made unbalanced by sampling, which is outlined in Section 7
2.1.1 Single Factor
Simplest structure - one grouping factor with multiple observations. Here we create a structure with 2 repeated observations of 5 individuals (small number are used here simply for illustration purposes). The structure contains the name of the grouping factors and their sample sizes, and repeat_obs is the number of repeated observations.
make_structure(structure="individual(5)", repeat_obs=2)## individual
## 1 1
## 2 1
## 3 2
## 4 2
## 5 3
## 6 3
## 7 4
## 8 4
## 9 5
## 10 52.1.2 Nested factors
If we want to have nested factors, so different hierarchical groups, where levels of one group only exist in one higher group then we can use the / symbol in the structure argument. For example, here we have 2 sexes, each with 5 individuals, with 2 repeated measurements each.
make_structure(structure="sex(2)/individual(5)", repeat_obs=2)## sex individual
## 1 1 1
## 2 1 1
## 3 1 2
## 4 1 2
## 5 1 3
## 6 1 3
## 7 1 4
## 8 1 4
## 9 1 5
## 10 1 5
## 11 2 6
## 12 2 6
## 13 2 7
## 14 2 7
## 15 2 8
## 16 2 8
## 17 2 9
## 18 2 9
## 19 2 10
## 20 2 10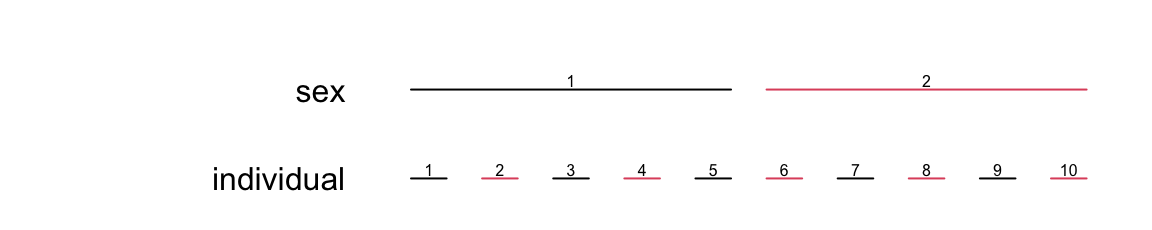
Note that in the nesting, the sample size for the lower group now represents the number within each level of the higher, rather than the total sample size, so overall there is 10 individuals.
We can nest as much as we want:
make_structure(structure="species(2)/population(2)/individual(2)", repeat_obs=2)## species population individual
## 1 1 1 1
## 2 1 1 1
## 3 1 1 2
## 4 1 1 2
## 5 1 2 3
## 6 1 2 3
## 7 1 2 4
## 8 1 2 4
## 9 2 3 5
## 10 2 3 5
## 11 2 3 6
## 12 2 3 6
## 13 2 4 7
## 14 2 4 7
## 15 2 4 8
## 16 2 4 8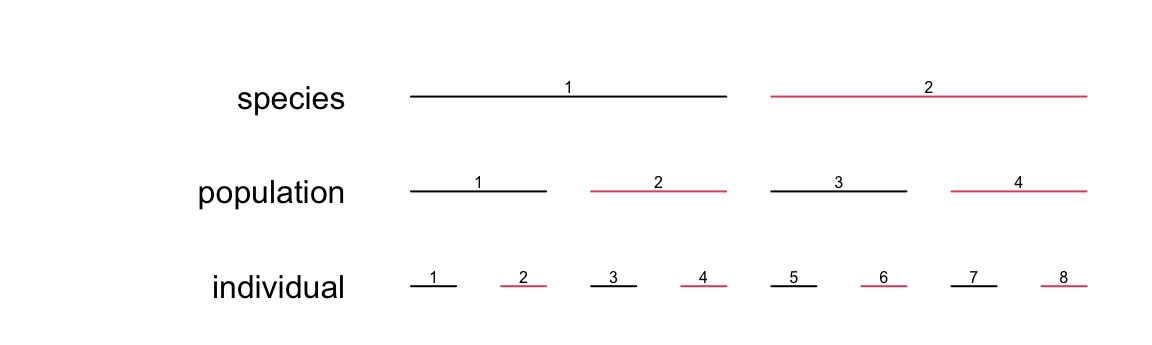
2.1.3 Crossed factors
We can create completely crossed factors - every combination of levels exists - using the + symbol in the structure argument
make_structure(structure="treatment(2) + individual(5)", repeat_obs=1)## treatment individual
## 1 1 1
## 2 1 2
## 3 1 3
## 4 1 4
## 5 1 5
## 6 2 1
## 7 2 2
## 8 2 3
## 9 2 4
## 10 2 5We can combine crossed and nested structures:
make_structure(structure="treatment(2) + sex(2)/individual(5)", repeat_obs=1)## treatment sex individual
## 1 1 1 1
## 2 1 1 2
## 3 1 1 3
## 4 1 1 4
## 5 1 1 5
## 6 1 2 6
## 7 1 2 7
## 8 1 2 8
## 9 1 2 9
## 10 1 2 10
## 11 2 1 1
## 12 2 1 2
## 13 2 1 3
## 14 2 1 4
## 15 2 1 5
## 16 2 2 6
## 17 2 2 7
## 18 2 2 8
## 19 2 2 9
## 20 2 2 10We can also output the crossed and nested using :
make_structure(structure="treatment(2) + individual(5) + treatment:individual", repeat_obs=1)## treatment individual treatment_individual
## 1 1 1 1
## 2 1 2 2
## 3 1 3 3
## 4 1 4 4
## 5 1 5 5
## 6 2 1 6
## 7 2 2 7
## 8 2 3 8
## 9 2 4 9
## 10 2 5 102.1.4 Temporal structure
ds <- make_structure(structure="year(2)/month(12)/day(30)", repeat_obs=1)
head(ds)## year month day
## 1 1 1 1
## 2 1 1 2
## 3 1 1 3
## 4 1 1 4
## 5 1 1 5
## 6 1 1 6ds <- make_structure(structure="year(2) + month(12) + day(30) + year:month:day", repeat_obs=1)
head(ds)## year month day year_month_day
## 1 1 1 1 1
## 2 1 1 2 2
## 3 1 1 3 3
## 4 1 1 4 4
## 5 1 1 5 5
## 6 1 1 6 62.1.5 Naming factor levels
Rather than just outputting 1 - N levels for the level names of each factor, we might want to assign names.
This can be done for all or some of the grouping factors, using the level_names argument. We can input a list, with an item in the list for each grouping factor we want to assign names, and then a vector of their names, which is the same length of the number of levels in that grouping factor. For example, below we just assign names to the two sexes:
make_structure(structure="sex(2)/individual(5)", repeat_obs=2, level_names=list(sex=c("female","male")))## sex individual
## 1 female 1
## 2 female 1
## 3 female 2
## 4 female 2
## 5 female 3
## 6 female 3
## 7 female 4
## 8 female 4
## 9 female 5
## 10 female 5
## 11 male 6
## 12 male 6
## 13 male 7
## 14 male 7
## 15 male 8
## 16 male 8
## 17 male 9
## 18 male 9
## 19 male 10
## 20 male 10And then to the individuals and the sexes
make_structure(structure="sex(2)/individual(5)", repeat_obs=2, level_names=list(sex=c("female","male"),individual=paste0("ind_",1:10)))## sex individual
## 1 female ind_1
## 2 female ind_1
## 3 female ind_2
## 4 female ind_2
## 5 female ind_3
## 6 female ind_3
## 7 female ind_4
## 8 female ind_4
## 9 female ind_5
## 10 female ind_5
## 11 male ind_6
## 12 male ind_6
## 13 male ind_7
## 14 male ind_7
## 15 male ind_8
## 16 male ind_8
## 17 male ind_9
## 18 male ind_9
## 19 male ind_10
## 20 male ind_10